MD
From NWChem
Molecular dynamics
Introduction
Spacial decomposition
The molecular dynamics module of NWChem uses a distribution of data based on a spacial decomposition of the molecular system, offering an efficient parallel implementation in terms of both memory requirements and communication costs, especially for simulations of large molecular systems.
Inter-processor communication using the global array tools and the design of a data structure allowing distribution based on spacial decomposition are the key elements in taking advantage of the distribution of memory requirements and computational work with minimal communication.
In the spacial decomposition approach, the physical simulation volume is divided into rectangular cells, each of which is assigned to a processor. Depending on the conditions of the calculation and the number of available processors, each processor contains one or more of these spacially grouped cells. The most important aspects of this decomposition are the dependence of the cell sizes and communication cost on the number of processors and the shape of the cells, the frequent reassignment of atoms to cells leading to a fluctuating number of atoms per cell, and the locality of communication which is the main reason for the efficiency of this approach for very large molecular systems.
To improve efficiency, molecular systems are broken up into separately treated solvent and solute parts. Solvent molecules are assigned to the domains according to their center of geometry and are always owned by a one node. This avoids solvent-solvent bonded interactions crossing node boundaries. Solute molecules are broken up into segments, with each segment assigned to a processor based on its center of geometry. This limits the number of solute bonded interactions that cross node boundaries. The processor to which a particular cell is assigned is responsible for the calculation of all interactions between atoms within that cell. For the calculation of forces and energies in which atoms in cells assigned to different processors are involved, data are exchanged between processors. The number of neighboring cells is determined by the size and shape of the cells and the range of interaction. The data exchange that takes place every simulation time step represents the main communication requirements. Consequently, one of the main efforts is to design algorithms and data structures to minimize the cost of this communication. However, for very large molecular systems, memory requirements also need to be taken into account.
To compromise between these requirements exchange of data is performed in successive point to point communications rather than using the shift algorithm which reduces the number of communication calls for the same amount of communicated data.
For inhomogeneous systems, the computational load of evaluating atomic interactions will generally differ between cell pairs. This will lead to load imbalance between processors. Two algorithms have been implemented that allow for dynamically balancing the workload of each processor. One method is the dynamic resizing of cells such that cells gradually become smaller on the busiest node, thereby reducing the computational load of that node. Disadvantages of this method are that the efficiency depends on the solute distribution in the simulation volume and the redistribution of work depends on the number of nodes which could lead to results that depend on the number of nodes used. The second method is based on the dynamic redistribution of intra-node cell-cell interactions. This method represents a more coarse load balancing scheme, but does not have the disadvantages of the cell resizing algorithm. For most molecular systems the cell pair redistribution is the more efficient and preferred method.
The description of a molecular system consists of static and dynamic information. The static information does not change during a simulation and includes items such as connectivity, excluded and third neighbor lists, equilibrium values and force constants for all bonded and non-bonded interactions. The static information is called the topology of the molecular system, and is kept on a separate topology file. The dynamic information includes coordinates and velocities for all atoms in the molecular system, and is kept in a so-called restart file.
Topology
The static information about a molecular system that is needed for a molecular simulation is provided to the simulation module in a topology file. Items in this file include, among many other things, a list of atoms, their non-bonded parameters for van der Waals and electrostatic interactions, and the complete connectivity in terms of bonds, angles and dihedrals.
In molecular systems, a distinction is made between solvent and solute, which are treated separately. A solvent molecule is defined only once in the topology file, even though many solvent molecules usually are included in the actual molecular system. In the current implementation only one solvent can be defined. Everything that is not solvent in the molecular system is solute. Each solute atom in the system must be explicitly defined in the topology.
Molecules are defined in terms of one or more segments. Typically, repetitive parts of a molecule are each defined as a single segment, such as the amino acid residues in a protein. Segments can be quite complicated to define and are, therefore, collected in a set of database files. The definition of a molecular system in terms of segments is a sequence.
Topology files are created using the prepare module.
Files
File names used have the form system_calc.ext, with exception of the topology file, which is named system.top. Anything that refers to the definition of the chemical system can be used for system, as long as no periods or underlines are used. The identifier calc can be anything that refers to the type of calculation to be performed for the system with the topology defined. This file naming convention allows for the creation of a single topology file system.top that can be used for a number of different calculations, each identified with a different calc. For example, if crown.top is the name of the topology file for a crown ether, crown_em, crown_md, crown_ti could be used with appropriate extensions for the filenames for energy minimization, molecular dynamics simulation and multi-configuration thermodynamic integration, respectively. All of these calculations would use the same topology file crown.top.
The extensions <ext> identify the kind of information on a file, and are pre-determined.
| dbg | debug file |
| frg | fragment file |
| gib | free energy data file |
| mri | free energy multiple run input file |
| mro | free energy multiple run output file |
| nw | NWChem input file |
| nwout | NWChem output file |
| out | molecular dynamics output file |
| pdb | PDB formatted coordinate file |
| prp | property file |
| qrs | quenched restart file, resulting from an energy minimization |
| rst | restart file, used to start or restart a simulation |
| seq | sequence file, describing the system in segments |
| sgm | segment file, describing segments |
| syn | synchronization time file |
| tst | test file |
| tim | timing analysis file |
| top | topology file, contains the static description of a system |
| trj | trajectory file |
Databases
Database file supplied with NWChem and used by the prepare module are found in directories with name ffield_level, where ffield is any of the supported force fields. The source of the data is identified by level, and can be
| level | Description |
| s | original published data |
| x | additional published data |
| q | contributed data |
| u | user preferred data |
| t | user defined temporary data |
The user is can replace these directories or add additional database files by specifying them in the .nwchemrc file. or in the prepare input file.
The extension 1-9 defines the priority of database file.
| frg | fragments |
| par | parameters |
| seq | sequences |
| sgm | segments |
Force fields
Force fields recognized are
| Keyword | Force field | Status |
| amber | AMBER99 | AMBER95,GLYCAM also available |
| charmm | CHARMM |
Format of fragment files
Fragment files contain the basic information needed to specify all interactions that need to be considered in a molecular simulation. Normally these files are created by the prepare module. Manual editing is needed when, for example, the prepare module could not complete atom typing, or when modified charges are required.
Creating segment files
The prepare module is used to generate segment files from corresponding fragment files. A segment file contains all information for the calculation of bonded and non-bonded interactions for a given chemical system using a specific force field.
Which atoms form a fragment is specified in the coordinate file, currently only in PDB format. The segment entries define three sets of parameters for each interaction.
Free energy perturbations can be performed using set 1 for the generation of the ensemble while using sets 2 and/or 3 as perturbations. Free energy multiconfiguration thermodynamic integration and multistep thermodynamic perturbation calculations are performed by gradually changing the interactions in the system from parameter set 2 to parameter set 3. These modifications can be edited into the segment files manually, or introduced directly into the topology file using the modify commands in the input for the prepare module.
Creating sequence files
A sequence file describes a molecular system in terms of segments. This file is generated by the prepare module for the molecular system provided on a PDB-formatted coordinate file
Creating topology files
The topology describes all static information that describes a molecular system. This includes the connectivity in terms of bond-stretching, angle-bending and torsional interactions, as well as the non-bonded van der Waals and Coulombic interactions.
The topology of a molecular system is generated by the prepare module from the sequence in terms of segments as specified on the PDB file. For each unique segment specified in this file the segment database directories are searched for the segment definition. For segments not found in one of the database directories a segment definition is generated in the temporary directory if a fragment file was found. If a fragment file could not be found, it is generated by the prepare module base on what is found on the PDB file.
When all segments are found or created, the parameter substitutions are performed, using force field parameters taken from the parameter databases. After all lists have been generated the topology is written to a local topology file <system>.top.
Creating restart files
Restart files contain all dynamical information about a molecular system and are created by the prepare module if a topology file is available. The prepare module will automatically generate coordinates for hydrogen atoms and monatomic counter ions not found on the PDB formatted coordinate file, if no fragment or segment files were generated using that PDB file.
The prepare module has a number of other optional input command, including solvation.
Molecular simulations
The type of molecular dynamics simulation is specified by the NWChem task directive.
task md [ energy | optimize | dynamics | thermodynamics ]
where the theory keyword md specifies use of the molecular dynamics module, and the operation keyword is one of
- energy for single configuration energy evaluation
- optimize for energy minimization
- dynamics for molecular dynamics simulations and single step thermodynamic perturbation free energy molecular dynamics simulations
- thermodynamics for combined multi-configuration thermodynamic integration and multiple step thermodynamic perturbation free energy molecular dynamics simulations.
System specification
The chemical system for a calculation is specified in the topology and restart files. These files should be created using the utilities nwtop and nwrst before a simulation can be performed. The names of these files are determined from the required system directive.
system <string systemid>_<string calcid>
where the strings systemid and calcid are user defined names for the chemical system and the type of calculation to ber performed, respectively. These names are used to derive the filenames used for the calculation. The topoly file used will be systemid.top, while all other files are named systemid_calcid.ext.
Restarting and continuing simulations
finish
Specifies that the current job will finish a previous, incomplete simulation, using the input data that have been recorded by that previous run in the restart file. Most of the input in the current md input block will be ignored.
resume
Specifies that the current job will be an extension of a previous simulation, using most of the input data that have been recorded by that previous run in the restart file. Typically the input in the current md input block defines a larger number of steps than the previous job.
Parameter set
set <integer iset>
Specifies the use of parameter set <iset> for the molecular dynamics simulation. The topology file contains three separate parameters sets that can be used. The default for <iset> is 1.
lambda <integer ilambda> <integer ilambda>
Specifies the use of parameter set for the ilambda-th of mlambda steps.
pset <integer isetp1> [<integer isetp2>]
Specifies the parameter sets to be used as perturbation potentials in single step thermodynamic perturbation free energy evaluations, where <isetp1> specifies the first perturbation parameter set and <isetp2> specifies the second perturbation parameter set. Legal values for <isetp1> are 2 and 3. Legal value for <isetp2> is 3, in which case <isetp1> can only be 2. If specified, <iset> is automatically set to 1.
pmf [ equilharm <integer npmfc> | scale <real facpmf>]
Specifies that any potential of mean force functions defined in the topology files are to be used. If equilharm is specified, the first npmfc dynamics steps will use a harmonic potential in stead of any pmf constraint. If scale is specified, all pmf force constants are scaled by a factor facpmf.
distar [draver [<integer ndaver default 1>]] [scale <real drsscl>] [after <integer nfdrss>]
Specifies that any distance restraint functions defined in the topology files are to be used.
qhop [<integer nfhop default 10>] [<real rhop default 0.35>] [<real thop default 0.02>]
Specifies that a Q-HOP simulation is to be carried out with attempted proton hops every nfhop steps, a cutoff for the donor-acceptor pair distance of rhop nm, and a minimum time before back hopping can occur of thop ps.
Energy minimization algorithms
The energy minimization of the system as found in the restart file is performed with the following directives. If both are specified, steepest descent energy minimization precedes conjugate gradient minimization.
sd <integer msdit> [init <real dx0sd>] [min <real dxsdmx>] \
[max <real dxmsd>]
Specifies the variables for steepest descent energy minimizations, where <msdit> is the maximum number of steepest descent steps taken, for which the default is 100, <dx0sd> is the initial step size in nm for which the default is 0.001, <dxsdmx> is the threshold for the step size in nm for which the default is 0.0001, and <dxmsd> is the maximum allowed step size in nm for which the default is 0.05.
cg <integer mcgit> [init <real dx0cg>] [min <real dxcgmx>] \
[cy <integer ncgcy>]
Specifies the variables for conjugate gradient energy minimizations, where <mcgit> is the maximum number of conjugate gradient steps taken, for which the default is 100, <dx0cg> is the initial search interval size in nm for which the default is 0.001, <dxcgmx> is the threshold for the step size in nm for which the default is 0.0001, and <ncgcy> is the number of conjugate gradient steps after which the gradient history is discarded for which the default is 10. If conjugate gradient energy minimization is preceded by steepest descent energy minimization, the search interval is set to twice the final step of the steepest descent energy minimization.
Multi-configuration thermodynamic integration
The following keywords control free energy difference simulations. Multi-configuration thermodynamic integrations are always combined with multiple step thermodynamic perturbations.
(forward | reverse) [[<integer mrun> of] <integer maxlam>]
Specifies the direction and number of integration steps in free energy evaluations, with forward being the default direction. <mrun> is the number of ensembles that will be generated in this calculation, and <maxlam> is the total number of ensembles to complete the thermodynamic integration. The default value for <maxlam> is 21. The default value of <mrun> is the value of <maxlam>.
error <real edacq>
Specifies the maximum allowed statistical error in each generated ensemble, where <edacq> is the maximum error allowed in the ensemble average derivative of the Hamiltonian with respect to $\lambda$ with a default of 5.0 kJmol − 1.
drift <real ddacq>
Specifies the maximum allowed drift in the free energy result, where <ddacq> is the maximum drift allowed in the ensemble average derivative of the Hamiltonian with respect to λ with a default of 5.0 kJmol − 1ps − 1.
factor <real fdacq>
Specifies the maximum allowed change in ensemble size where <fdacq> is the minimum size of an ensemble relative to the previous ensemble in the calculation with a default value of 0.75.
decomp
Specifies that a free energy decomposition is to be carried out. Since free energy contributions are path dependent, results from a decomposition analysis can no be unambiguously interpreted, and the default is not to perform this decomposition.
sss [delta <real delta>]
Specifies that atomic non-bonded interactions describe a dummy atom in either the initial or final state of the thermodynamic calculation will be calculated using separation-shifted scaling, where <delta> is the separation-shifted scaling factor with a default of 0.075nm2. This scaling method prevents problems associated with singularities in the interaction potentials.
new | renew | extend
Specifies the initial conditions for thermodynamic calculations. new indicates that this is an initial mcti calculation, which is the default. renew instructs to obtain the initial conditions for each λ from the mro-file from a previous mcti calculation, which has to be renamed to an mri-file. The keyword extend will extend a previous mcti calculation from the data read from an mri-file.
Time and integration algorithm directives
Following directives control the integration of the equations of motion.
leapfrog | leapfrog_bc
Specifies the integration algorithm, where leapfrog specifies the default leap frog integration, and leapfrog_bc specifies the Brown-Clarke leap frog integrator.
guided [<real fguide default 0.2> [<real tguide default 0.2>]]
Specifies the use of the guided molecular dynamics simulation technique. Variable fguide defines the fraction of the averaged forces g to be added to the forces ff evaluated using the force field functions to obtain the forces f used to advance the coordinates.
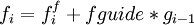
Variable tguide defines the length of the averaging relative to the timestep Δ t.
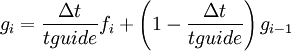
The current implementation is still under development.
equil <integer mequi>
Specifies the number of equilibration steps <mequi>, with a default of 100.
data <integer mdacq> [over <integer ldacq>]]
Specifies the number of data gathering steps <mdacq> with a default of 500. In multi-configuration thermodynamic integrations <mequi> and <mdacq> are for each of the ensembles, and variable <ldacq> specifies the minimum number of data gathering steps in each ensemble. In regular molecular dynamics simulations <ldacq> is not used. The default value for <ldacq> is the value of <mdacq>.
time <real stime>
Specifies the initial time <stime> of a molecular simulation in ps, with a default of 0.0.
step <real tstep>
Specifies the time step <tstep> in ps, with 0.001 as the default value.
Ensemble selection
Following directives control the ensemble type.
isotherm [<real tmpext> [<real tmpext2>]] [trelax <real tmprlx> [<real tmsrlx>]] \
[anneal [<real tann1>] <real tann2>]
Specifies a constant temperature ensemble using Berendsen's thermostat, where <tmpext> is the external temperature with a default of 298.15 K, and <tmprlx> and <tmsrlx> are temperature relaxation times in ps with a default of 0.1. If only <tmprlx> is given the complete system is coupled to the heat bath with relaxation time <tmprlx>. If both relaxation times are supplied, solvent and solute are independently coupled to the heat bath with relaxation times <tmprlx> and <tmsrlx>, respectively. If keyword anneal is specified, the external temperature will change from tmpext to tempext2 between simulation time tann1 and tann2
isobar [<real prsext>] [trelax <real prsrlx> ] \
[compress <real compr>] [anisotropic] [xy | z | xy-z]
Specifies a constant pressure ensemble using Berendsen's piston, where <prsext> is the external pressure with a default of 1.025105Pa, <prsrlx> is the pressure relaxation time in ps with a default of 0.5, and <compr> is the system compressibility in m2N − 1 with a default of 4.53E-10. Optional keywords xy, z and xy-z may be used to specify that pressure scaling is to be applied in the x and y dimension only, the z dimension only, or, in all three dimensions with identical scaling in the x and y dimension. The last option requires that anisotropic is also specified.
Velocity reassignments
Velocities can be periodically reassigned to reflect a certain temperature.
vreass <integer nfgaus> <real tgauss>
[fraction [<real frgaus default 0.5]]
[once]
[(first | initial)] [(last | final)]
Specifies that velocities will be reassigned every <nfgaus> molecular dynamics steps, reflecting a temperature of <tgauss> K. The default is not to reassign velocities, i.e. <nfgaus> is 0. Keyword fraction allows the specification of the fraction of the new velocities are random. Keyword once specifies that velocity reassignment only should be done in the first step. Keywords first or initial and last or final specify that velocity reassigment should only be applied in the first and last window of multiple run simulations.
Cutoff radii
Cutoff radii can be specified for short range and long range interactions.
cutoff [short] <real rshort> [long <real rlong>] \
[qmmm <real rqmmm>]
Specifies the short range cutoff radius <rshort>, and the long range cutoff radius <rlong> in nm. If the long range cutoff radius is larger than the short range cutoff radius the twin range method will be used, in which short range forces and energies are evaluated every molecular dynamics step, and long range forces and energies with a frequency of <nflong> molecular dynamics steps. Keyword qmmm specifies the radius of the zone around quantum atoms defining the QM/MM bare charges. The default value for <rshort>, <rlong> and <rqmmm> is 0.9 nm.
Polarization
First order and self consistent electronic polarization models have been implemented.
polar (first | scf [[<integer mpolit>] <real ptol>])
Specifies the use of polarization potentials, where the keyword first specifies the first order polarization model, and scf specifies the self consistent polarization field model, iteratively determined with a maximum of <mpolit> iterations to within a tolerance of <ptol> D in the generated induced dipoles. The default is not to use polarization models.
External electrostatic field
field <real xfield> [freq <real xffreq>] [vector <real xfvect(1:3)>]
Specifies an external electrostatic field, where <xfield> is the field strength, <xffreq> is the frequency in MHz and <xfvect> is the external field vector.
Constraints
Constraints are satisfied using the SHAKE coordinate resetting procedure.
shake [<integer mshitw> [<integer mshits>]] \
[<real tlwsha> [<real tlssha>]]
Specifies the use of SHAKE constraints, where <mshitw> is the maximum number of solvent SHAKE iterations, and <mshits> is the maximum number of solute SHAKE iterations. If only <mshitw> is specified, the value will also be used for <mshits>. The default maximum number of iterations is 100 for both. <tlwsha> is the solvent SHAKE tolerance in nm, and <tlssha> is the solute SHAKE tolerance in nm. If only <tlwsha> is specified, the value given will also be used for <tlssha>. The default tolerance is 0.001 nm for both.
noshake (solvent | solute)
Disables SHAKE and treats the bonded interaction according to the force field.
Long range interaction corrections
Long range electrostatic interactions are implemented using the smooth particle mesh Ewald technique, for neutral periodic cubic systems in the constant volume ensemble, using pair interaction potentials. Particle-mesh Ewald long range interactions can only be used in molecular dynamics simulations using effective pair potentials, and not in free energy simulations, QMD or QM/MM simulations.
pme [grid <integer ng>] [alpha <real ealpha>] \
[order <integer morder>] [fft <integer imfft>]\
[procs <integer nprocs>] [solvent]
Specifies the use of smooth particle-mesh Ewald long range interaction treatment, where ng is the number of grid points per dimension, ealpha is the Ewald coefficient in nm − 1, with a default that leads to a tolerance of 10 − 4 at the short range cutoff radius, and morder is order of the Cardinal B-spline interpolation which must be an even number and at least 4 (default value). A platform specific 3D fast Fourier transform is used, if available, when imfft is set to 2. nprocs can be used to define a subset of processors to be used to do the FFT calculations. If solvent is specified, the charge grid will be calculated from the solvent charges only.
react [<real dielec default 80.0>]
Specifies that a simple reaction field correction is used with a dielectric constant dielec. This is an experimental option that has not been well tested.
Fixing coordinates
Solvent or solute may be fixed using the following keywords.
( fix | free )
solvent ( [<integer idfirst> [<integer idlast>]] |
( within | beyond) <real rfix> <string atomname> ) | \
solute ( [<integer idfirst> [<integer idlast>]] [ heavy | {<string atomname>}] |
( within | beyond) <real rfix> <string atomname> )
[permanent]
For solvent the molecule numbers idfirst and idlastmay be specified to be the first and last molecule to which the directive applies. If omitted, the directive applies to all molecules. For solute, the segment numbers idfirst and idlastmay be specified to be the first and last segment to which the directive applies. If omitted, the directive applies to all segments. In addition, the keyword heavy may be specified to apply to all non hydrogen atoms in the solute, or a set of atom names may be specified in which a wildcard character ? may be used. Keyword permanent is used to keep the specification on the restart file for subsequent simulations.
Special options
import [<integer impfr default 1> [<integer impto default impfr> \
[<integer nftri default 1>]]]
Specifies the import of frames impfr to impto with frequency nftri from a trajectory file with extension tri for which energies and forces are to be recalculated. This option only applied to task md energy.
detail
Specifies that moments of inertia and radii of gyration will be part of the recorded properties.
profile
Specifies that execution time profiling data will be part of the recorded properties.
scale <real scaleq>
Specifies that all charges will be scaled by the factro scaleq.
collapse [<real fcoll default 10.0> [ segment | z | xy ]
Specifies that additional forces directed to the origin of the simulation cell with strength fcoll will be applied to all solute molecules. If z or xy is specified, these forces will only apply in the specified dimension(s).
include fixed
Specifies that energies will be evaluated between fixed atoms. Normally these interactions are excluded from the pairlists.
eqm <real eqm>
Specifies the zero point of energy in QMD simulations.
atomlist
Specifies that pairlists will be atom based. Normally pairlist are charge group based.
Autocorrelation function
For the evaluation of the statistical error of multi-configuration thermodynamic integration free energy results a correlated data analysis is carried out, involving the calculation of the autocorrelation function of the derivative of the Hamiltonian with respect to the control variable $\lambda$.
auto <integer lacf> [fit <integer nfit>] [weight <real weight>]
Controls the calculation of the autocorrelation, where <lacf> is the length of the autocorrelation function, with a default of 1000, <nfit> is the number of functions used in the fit of the autocorrelation function, with a default of 15, and <weight> is the weight factor for the autocorrelation function, with a default value of 0.0.
Print options
Keywords that control print to the output file, with extension out. Print directives may be combined to a single directive.
print [topol [nonbond] [solvent] [solute]] \
[step <integer nfoutp> [extra] [energy]] \
[stat <integer nfstat>] \
[energies [<integer nfener>]] \
[forces [<integer nfforce>]] \
[matrix] \
[expect <integer npxpct>] \
[timing] \
[pmf [<integer iprpmf>]] \
[out6] \
[dayout]
- Keyword topol specifies printing the topology information, where nonbond refers to the non-bonded interaction parameters, solvent to the solvent bonded parameters, and solute to the solute bonded parameters. If only topol is specified, all topology information will be printed to the output file.
- Keyword step specifies the frequency nfoutp of printing molecular dynamics step information to the output file. If the keyword extra is specified additional energetic data are printed for solvent and solute separately. If the keyword energy is specified, information is printed for all bonded solute interactions. The default for nfoutp is 0. For molecular dynamics simulations this frequency is in time steps, and for multi-configuration thermodynamic integration in λ-steps.
- Keyword stat specifies the frequency <nfstat> of printing statistical information of properties that are calculated during the simulation. For molecular dynamics simulation this frequency is in time steps, for multi-configuration thermodynamic integration in λ-steps.
- Keyword energies specifies the frequency nfener of printing solute bonded energies the output file for energy/import calculations. The default for nfener is 0.
- Keyword forces specifies the frequency nfforc of printing solute forces the output file for energy/import calculations. The default for nfforc is 0.
- Keyword matrix specifies that a solute distance matrix is to be printed.
- Keyword expect is obsolete.
- Keyword timing specifies that timing data is printed.
- Keyword pmf specifies that pmf data is printed every iprpmf steps. Keyword out6 specifies that output is written to standard out in stead of the output file with extension out.
- Keyword dayout is obsolete.
Periodic updates
Following keywords control periodic events during a molecular dynamics or thermodynamic integration simulation. Update directives may be combined to a single directive.
update [pairs <integer nfpair default 1>] \
[long <integer nflong default 1>] \
[center <integer nfcntr default 0> [zonly | xyonly] \
[fraction <integer idscb(1:5)>] \
[motion <integer nfslow default 0>] \
[analysis <integer nfanal default 0>] \
[rdf <integer nfrdf default 0> \
[range <real rrdf>] [bins <integer ngl>] \
- Keyword pairs specifies the frequency <nfpair> in molecular dynamics steps of updating the pair lists. The default for the frequency is 1. In addition, pair lists are also updated after each step in which recording of the restart or trajectory files is performed. Updating the pair lists includes the redistribution of atoms that changed domain and load balancing, if specified.
- Keyword long specifies the frequency <nflong> in molecular dynamics steps of updating the long range forces. The default frequency is 1. The distinction of short range and long range forces is only made if the long range cutoff radius was specified to be larger than the short range cutoff radius. Updating the long range forces is also done in every molecular dynamics step in which the pair lists are regenerated.
- Keywrod center specifies the frequency <nfcntr> in molecular dynamics steps in which the center of geometry of the solute(s) is translated to the center of the simulation volume. Optional keyword zonly or xyonly can be used to specify that centering will take place in the z-direction or in the xy-plane only. The solute fractions determining the solutes that will be centered are specified by the keyword fraction and the vector <idscb>, with a maximum of 5 entries. This translation is implemented such that it has no effect on any aspect of the simulation. The default is not to center, i.e. nfcntr is 0. The default fraction used to center solute is 1.
- Keyword motion specifies the frequency <nfslow> in molecular dynamics steps of removing the overall rotational and center of mass translational motion.
- Keyword analysis specifies the frequency <nfanal> in molecular dynamics steps of invoking the analysis module. This option is obsolete.
- Keyword rdf specifies the frequency <nfrdf> in molecular dynamics steps of calculating contributions to the radial distribution functions. The default is 0. The range of the radial distribution functions is given by <rrdf> in nm, with a default of the short range cutoff radius. Note that radial distribution functions are not evaluated beyond the short range cutoff radius. The number of bins in each radial distribution function is given by <ngl>, with a default of 1000. This option is no longer supported. If radial distribution function are to be calculated, a rdi files needs to be available in which the contributions are specified as follows.
| Card | Format | Description |
| I-1 | i | Type, 1=solvent-solvent, 2=solvent-solute, 3-solute-solute |
| I-2 | i | Number of the rdf for this contribution |
| I-3 | i | First atom number |
| I-4 | i | Second atom number |
Recording
The following keywords control recording data to file. Record directives may be combined to a single directive.
record [rest <integer nfrest> [keep]] \
[coord <integer nfcoor default 0>] \
[wcoor <integer nfwcoo default 0>] \
[scoor <integer nfscoo default 0>] \
[veloc <integer nfvelo default 0>] \
[wvelo <integer nfwvel default 0>] \
[svelo <integer nfsvel default 0>] \
[force <integer nfvelo default 0>] \
[wforc <integer nfwvel default 0>] \
[sforc <integer nfsvel default 0>] \
[(prop | prop_average) <integer nfprop default 0>] \
[free <integer nffree default 1>] \
[sync <integer nfsync default 0>] \
[times <integer nftime default 0>] \
[acf] [cnv] [fet]
[binary] [ascii] [ecce] [argos]
- Keyword rest specifies the frequency <nfrest> in molecular dynamics steps of rewriting the restart file, with extension rst. For multi-configuration thermodynamic integration simulations the frequency is in steps in $\lambda$. The default is not to record. The restart file is used to start or restart simulations. The keyword keep causes all restart files written to be kept on disk, rather than to be overwritten.
- Keyword coord specifies the frequency <nfcoor> in molecular dynamics steps of writing coordinates to the trajectory file. This directive redefines previous coord, wcoor and scoor directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword wcoor specifies the frequency <nfcoor> in molecular dynamics steps of writing solvent coordinates to the trajectory file. This keyword takes precedent over coord. This directive redefines previous coord, wcoor and scoor directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword scoor specifies the frequency <nfscoo> in molecular dynamics steps of writing solute coordinates to the trajectory file. This keyword takes precedent over coord. This directive redefines previous coord, wcoor and scoor directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword veloc specifies the frequency <nfvelo> in molecular dynamics steps of writing velocities to the trajectory file. This directive redefines previous veloc, wvelo and svelo directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword wvelo specifies the frequency <nfvelo> in molecular dynamics steps of writing solvent velocitiesto the trajectory file. This keyword takes precedent over veloc. This directive redefines previous veloc, wvelo and svelo directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword svelo specifies the frequency <nfsvel> in molecular dynamics steps of writing solute velocities to the trajectory file. This keyword takes precedent over veloc. This directive redefines previous veloc, wvelo and svelo directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword force specifies the frequency <nfvelo> in molecular dynamics steps of writing forces to the trajectory file. This directive redefines previous vforce, wforc and sforc directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword wforc specifies the frequency <nfvelo> in molecular dynamics steps of writing solvent forcesto the trajectory file. This keyword takes precedent over force. This directive redefines previous vforce, wforc and sforc directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword sforc specifies the frequency <nfsvel> in molecular dynamics steps of writing solute forces to the trajectory file. This keyword takes precedent over force. This directive redefines previous vforce, wforc and sforc directives. The default is not to record.
- Keyword prop specifies the frequency <nfprop> in molecular dynamics steps of writing information to the property file, with extension prp. The default is not to record.
- Keyword prop_average specifies the frequency <nfprop> in molecular dynamics steps of writing average information to the property file, with extension prp. The default is not to record.
- Keyword free specifies the frequency <nffree> in multi-configuration thermodynamic integration steps to record data to the free energy data file, with extension gib. The default is 1, i.e. to record at every $\lambda$. This option is obsolete. All data are required to do the final analysis.
- Keyword sync specifies the frequency <nfsync> in molecular dynamics steps of writing information to the synchronization file, with extension syn. The default is not to record. The information written is the simulation time, the wall clock time of the previous MD step, the wall clock time of the previous force evaluation, the total synchronization time, the largest synchronization time and the node on which the largest synchronization time was found. The recording of synchronization times is part of the load balancing algorithm. Since load balancing is only performed when pair-lists are updated, the frequency <nfsync> is correlated with the frequency of pair-list updates <nfpair>. This directive is only needed for analysis of the load balancing performance. For normal use this directive is not used.
- Keyword times specifies the frequency <nfsync> in molecular dynamics steps of writing information to the timings file, with extension tim. The default is not to record. The information written is wall clock time used by each of the processors for the different components in the force evaluation. This directive is only needed for analysis of the wall clock time distribution. For normal use this directive is not used.
- Keywords acf, cnv and fet are obsolete.
- Keywords binary, ascii, ecce and argos are obsolete.
Program control options
load [reset]
( none |
size [<real factld>] |
sizez [<real factld>] | pairs |
(pairs [<integer ldpair>] size [<real factld>]) )
[last]
[minimum]
[average]
[combination]
[iotime]
[experimental]
Determines the type of dynamic load balancing performed, where the default is none. Load balancing option size is resizing cells on a node, and pairs redistributes the cell-cell interactions over nodes. Keyword reset will reset the load balancing read from the restart file. The level of cell resizing can be influenced with factld. The cells on the busiest node are resized with a factor
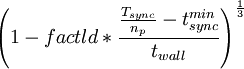
Where Tsync is the accumulated synchronization time of all nodes, np is the total number of nodes, 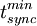 is the synchronization time of the busiest node, and twall is the wall clock time of the molecular dynamics step. For the combined load balancing, ldpair is the number of successive pair redistribution load balancing steps in which the accumulated synchronization time increases, before a resizing load balancing step will be attempted. Load balancing is only performed in molecular dynamics steps in which the pair-list is updated. The default load balancing is equivalent to specifying
is the synchronization time of the busiest node, and twall is the wall clock time of the molecular dynamics step. For the combined load balancing, ldpair is the number of successive pair redistribution load balancing steps in which the accumulated synchronization time increases, before a resizing load balancing step will be attempted. Load balancing is only performed in molecular dynamics steps in which the pair-list is updated. The default load balancing is equivalent to specifying
load pairs 10 size 0.75
Keyword last specifies that the load balancing is based on the synchronization times of the last step. This is the default. Keyword average specifies that the load balancing is based on the average synchronization times since the last load balancing step. Keyword minimum specifies that the load balancing is based on the minimum synchronization times since the last load balancing step. Keywords combination, iotime and experimental are experimental load balancing options that should not be used in production runs.
(pack | nopack)
Specifies if data are communicated in packed or unpacked form. The default is pack.
procs <integer npx> <integer npy> <integer npz>
Specifies the distribution of the available processors over the three Cartesian dimensions. The default distribution is chosen such that, <npx>*<npy>*<npz>=<np> and <npx> <= <npy> <= <npz>, where <npx>, <npy> and <npz> are the processors in the x, y and z dimension respectively, and <np> is the number of processors allocated for the calculation. Where more than one combination of <npx>, <npy> and <npz> are possible, the combination is chosen with the minimum value of <npx>+<npy>+<npz>. To change the default setting the following optional input option is provided.
cells <integer nbx> <integer nby> <integer nbz>
Specifies the distribution of cells, where <nbx>, <nby> and <nbz> are the number of cells in x, y and z direction, respectively. The molecular system is decomposed into cells that form the smallest unit for communication of atomic data between nodes. The size of the cells is per default set to the short-range cutoff radius. If long-range cutoff radii are used the cell size is set to half the long-range cutoff radius if it is larger than the short-range cutoff. If the number of cells in a dimension is less than the number of processors in that dimension, the number of cells is set to the number of processors.
extra <integer madbox>
Sets the number of additional cells for which memory is allocated. In rare events the amount of memory set aside per node is insufficient to hold all atomic coordinates assigned to that node. This leads to execution which aborts with the message that mwm or msa is too small. Jobs may be restarted with additional space allocated by where <madbox> is the number of additional cells that are allocated on each node. The default for <madbox> is 6. In some cases <madbox> can be reduced to 4 if memory usage is a concern. Values of 2 or less will almost certainly result in memory shortage.
mwm <integer mwmreq>
Sets the maximum number of solvent molecules <mwmreq> per node, allowing increased memory to be allocated for solvent molecules. This option can be used if execution aborted because mwm was too small.
msa <integer msareq>
Sets the maximum number of solute atoms <msareq> per node, allowing increased memory to be allocated for solute atoms. This option can be used if execution aborted because msa was too small.
mcells <integer mbbreq>
Sets the maximum number of cell pairs <mbbreq> per node, allowing increased memory to be allocated for the cell pair lists. This option can be used if execution aborted because mbbl was too small.
boxmin <real rbox>
Sets the minimum size of a cell. This directive is obsolete. The use of mcells is preferred.
segmentsize <real rsgm>
Sets the maximum size of a segment. This value is used to determine which segments at the boundary of the cutoff radius should be considered in the generation of the pairlists. This value is also determined by the prepare module and written to the restart file. Use of this directive is not needed for simulations that use the current prepare module to generate the restart file.
memory <integer memlim>
Sets a limit <memlim> in kB on the allocated amount of memory used by the molecular dynamics module. Per default all available memory is allocated. Use of this command is required for QM/MM simulations only.
expert
Enables the use of certain combinations of features that are considered unsafe. This directive should not be used for production runs.
develop <integer idevel>
Enables the use of certain development options specified by the integer idevel. This option is for development purposes only, and should not be used for production runs.
control <integer icntrl>
Enables the use of certain development options specified by the integer icntrl. This option is for development purposes only, and should not be used for production runs.
numerical
Writes out analytical and finite difference forces for test purposes.
server <string servername> <integer serverport>
Allows monitoring over a socket connection to the specified port on the named server of basic data as a simulation is running.
For development purposes debug information can be written to the debug file with extension dbg with
debug <integer idebug>
where idebug specifies the type of debug information being written.
For testing purposes test information can be written to the test file with extension tst with
test <integer itest>
where itest specifies the number of steps test information is written.
On some platforms prefetching of data can improve the efficiency. This feature can be turned on using
prefetch [<integer nbget>]
where nbget is the number of outstanding communication operations.
Application of periodic boundary conditions for the evaluation of forces can be controlled with
pbc ( atom | residue | molecule )
This option rarely needs to be used.
Autocorrelation functions for error analysis are controlled using
auto [ fit <integer iapprx> | weight <real weight> ]
This option is disabled in the current release.
Membrane system equilibration can be made more efficient using
membrane [ rotations ]
Constraining the center of mass of solute molecules in the xy plane is accomplished using
scmxy [<integer icmopt default 1>]
where icmopt determines if the constraint is mass weighted (2).
Radius of gyration calculations are enabled using
radius_gyration
Calculations of diffusion coefficients is enabled using
diffusion
This option is disabled in the current release.
comlim ( on | off )
is disabled
To limit the size of recoding files, new files are opened every nfnewf md steps using
batch <integer nfnewf>
